Events
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs and develops because of the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. Growth of the abnormal cells can interfere with normal lung function. It can pass from the original part of the lung to other parts of the body, such as the opposite lung, lymph nodes, bones, liver and more. Close to 9,000 cases of lung cancer were diagnosed in Singapore over a five year period of 2017 to 2021. It is the third most common cancer in men and women in Singapore. Lung cancer is also the leading cause of death for men and third cause of cancer death for women. Individuals above the age of 40 are more commonly diagnosed with lung cancer, however, the disease can also occur in younger individuals. It can develop over months and years and patients may not see the warning signs until much later.
Early detection can save lives. When detected in its early stages through proactive screening, lung cancer responds better to treatment. A Low-Dose Computerised Tomography (LDCT) scan is recommended for early lung cancer detection. The scan may take a minute or less, and it is not painful. The small amount of radiation used in LDCT screenings is much lower than standard doses for regular CT scans.
Lung cancer screenings can help to identify and diagnose cancer before symptoms occur. This is when the condition is more responsive to treatment. Screening at a younger age can also help increase the quality of life for those diagnosed.
Screening Criteria:
Do note that this sponsored screening is only for individuals who fulfil the criteria listed below:
- Individuals with Blue/Orange CHAS card
- 50-80 years old
- Smoked 20 pack years* and continuing to smoke OR quit less than 15 years ago
OR
- Individuals with Blue/Orange CHAS card
- 50-75 years old
- Family history of lung cancer (parents/child/siblings)
*How To Calculate Pack Years?
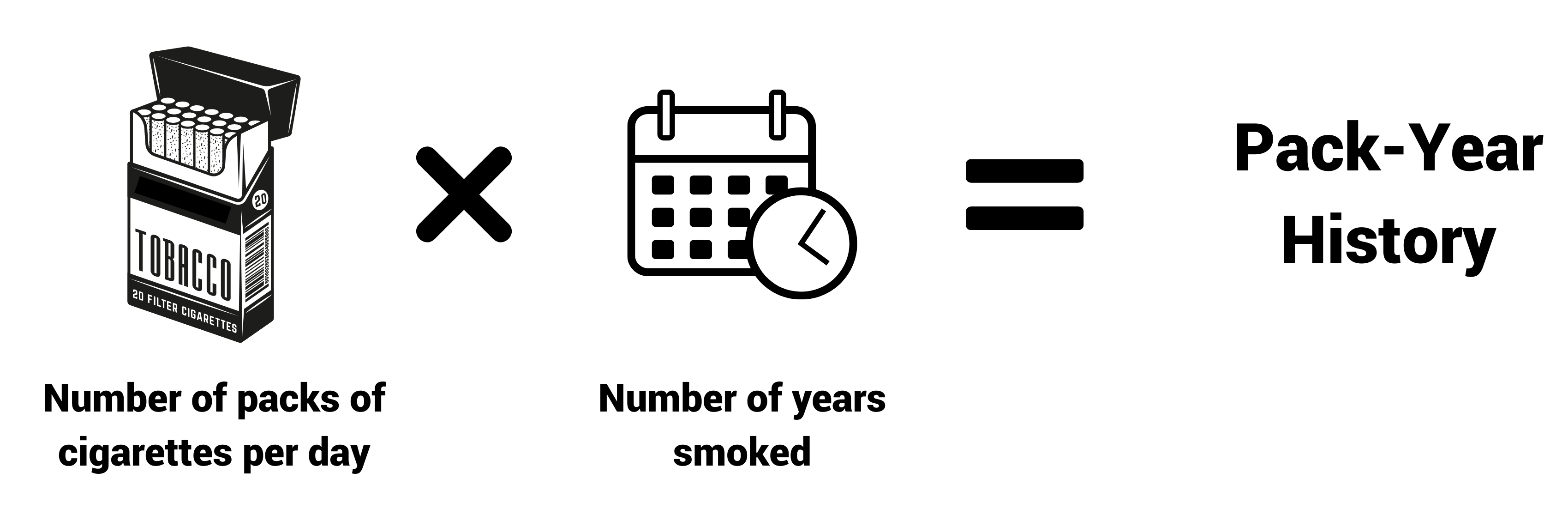
| Packs Per Day | Years | Pack Years |
| 1/2 (half pack) | 20 | 10 |
| 30 | 15 | |
| 40 or more | 20 | |
| 3/4 (three quarter pack) | 20 | 15 |
| 30 or more | 22.5 | |
| 1 | 10 | 10 |
| 20 or more | 20 | |
| 2 | 5 | 10 |
| 10 or more | 20 |
Registration for the Are You At Risk? Lung Cancer Screening is now closed.
Keep an eye out for the next campaign!
About Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs and develops because of the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. Cells lining the airway grow and divide without control, leading to the growth of an abnormal mass, interfering with normal lung function. It can pass from the original part of the lung to other parts of the body, such as the opposite lung, lymph nodes, bones, liver and more.
There are two main types of lung cancer:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLS)
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85-90% of all lung cancers. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) makes up about 10-15% of all lung cancer cases and is strongly associated with cigarette smoking. The major difference between these two types of lung cancer are the size and the shape of the cancer cell, forms of treatment and the speed at which the cancer spreads. Small Cell Lung Cancer spreads more rapidly.
With the rapid medical developments in recent years, there has been an overall improvement in the survival rate and disease outcome. Treatment of lung cancer can be complex, and is dependent on the type and the stage of lung cancer in an individual.
Signs and Symptoms
Individuals with early stage lung cancer may not experience any noticeable symptoms until much later. Common symptoms of advance-stage lung cancer include:
- Prolonged cough that worsen with time
- Shortness of breath
- Blood in coughed-up mucus
- Constant chest pain that may occur along with persistent cough
- Recurrent chest infection and fever
- Hoarseness
- New onset of wheezing
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Causes and Risk Factors
It is commonly known that smoking is the main risk factor for lung cancer. People who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer as they increase their risk with each cigarette they smoke as well as the number of years they smoke. However, non-smokers can also get the disease. One out of two lung cancer patients are non-smokers. This happens when non-smokers are exposed to second-hand smoke.
Some common factors that contribute to the risk of developing lung cancer include:
- Habitual smokers
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to cancer-causing asbestos, radon gas, coal gas and engine exhaust
- Family history of cancer (parents or siblings)
- Personal history of lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis
Speak to your doctor to understand your risk factors.
How To Prevent Lung Cancer?
Early detection can save lives. Lung cancer screenings can help to identify and diagnose cancer before symptoms occur. This is when the condition is more responsive to treatment. Screening at a younger age can also help increase the quality of life for those who are diagnosed.
Other ways to actively prevent lung cancer includes:
- Quit smoking
- Do not start smoking if you are a non-smoker
- Avoid secondhand smoke by staying away from areas where people are smoking
- Avoid carcinogens at work and in your daily life
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet
Screening Process
Step 1 – Register with 365CPS
Click on the “Register” button at the bottom of this page, complete and submit the online registration form.
Upon submission, our staff will respond to you in 5 working days.
Eligible individuals will receive a Confirmation Letter endorsed by 365CPS.
Step 2 – Schedule an Appointment
Once you receive the Confirmation Letter endorsed by 365CPS, kindly contact the selected clinic directly to schedule an appointment.
Kindly bring along your NRIC and Confirmation Letter for your appointment.
Step 3 – LDCT Scan
The appointment will involve an LDCT scan and a consultation with a doctor.
Step 4 – Post-Screening Consultation
Should your results indicate any abnormalities, a referral letter will be issued to refer you to a public health setting for further investigations.

