Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours (GIST)
What is GIST?
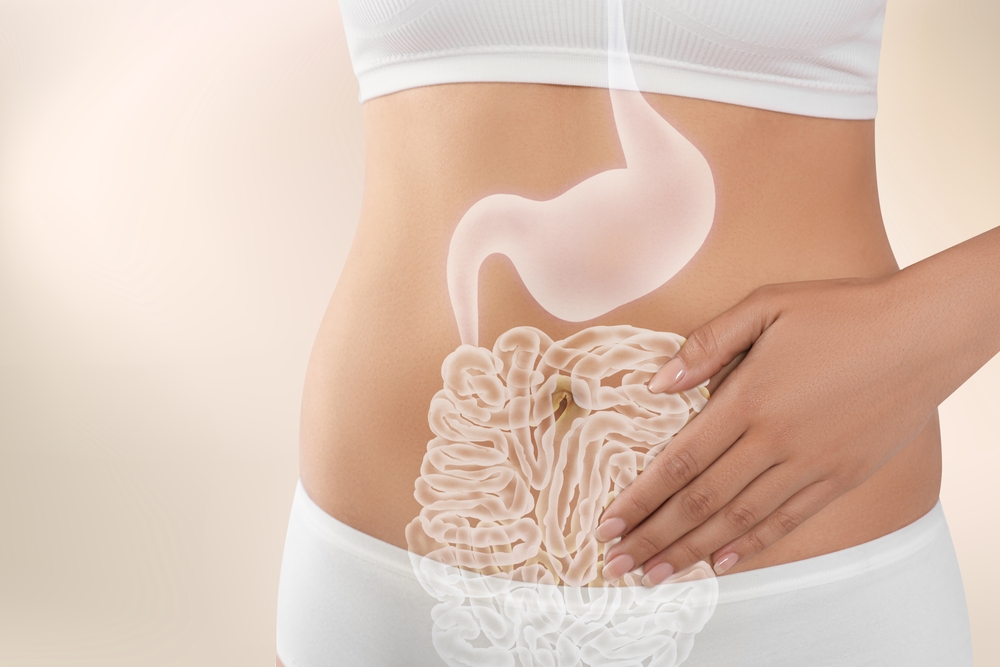
Gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) is a cancer affecting the digestive tract or nearby structures within the abdomen, most often presenting in the stomach or small intestine. The most common location of GIST is in the stomach (60%) and small intestines (30%) but can occur in any site in the digestive system.
Risk Factors
Most GISTs occur sporadically, without any known risk factors. A small percentage of GISTs may be associated with certain genetic syndromes, such as neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) or familial GIST syndrome.
Symptoms
GISTs can vary in size and location within the gastrointestinal tract, so symptoms may differ from one person to another. Common symptoms may include abdominal pain or discomfort, gastrointestinal bleeding (manifested as blood in the stool or black, tarry stools), anaemia, early satiety (feeling full after eating only a small amount), and unexplained weight loss.
Detection and Diagnosis
GIST is often incidentally found during investigation for unrelated problems. Imaging studies like contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or endoscopy may help detect GIST. A definitive diagnosis is usually made through biopsy of the tumor, either by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration or by surgical resection. The sample might be checked for certain changes in KIT and PDGFRA genes.
Treatment Options for GIST
Treatment typically involves surgical resection of the tumor, whenever possible. For inoperable or metastatic GISTs, targeted therapies such as imatinib have shown significant effectiveness in controlling the disease. In some cases, adjuvant therapy with imatinib may be recommended after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. Other targeted therapies, such as sunitinib, regorafenib and ripretinib are options for patients who don’t respond to imatinib or who develop resistance. Clinical trials may also be considered.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for understanding the nature of GIST, treatment options, potential side effects of medications, and the importance of regular follow-up, as GISTs can recur. Understanding GIST empowers patients to make informed decisions about their treatment and care.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, blood in the stool, or any concerning symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Timely medical evaluation is essential for early diagnosis and management.
This article is contributed by Dr Valerie Yang, Consultant Medical Oncologist at the National Cancer Centre Singapore. We acknowledge Specialised Therapeutics for supporting and facilitating this article.