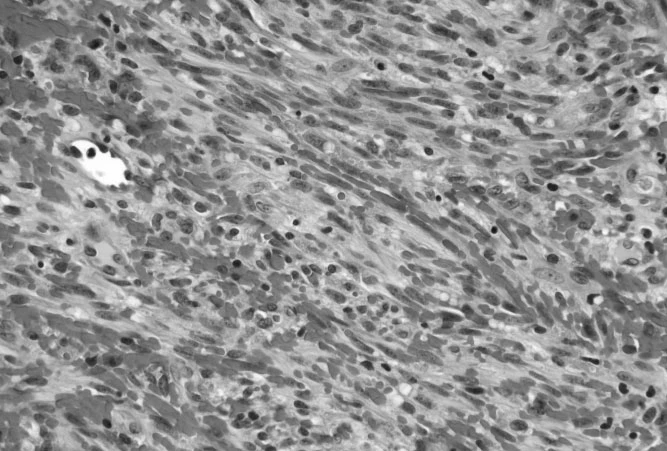
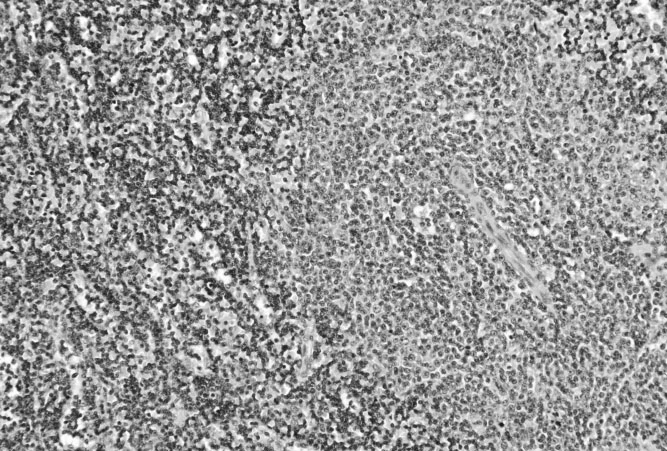
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a group of diseases characterised by abnormal cell growth. Humans are made up of cells, and these cells contain genes which direct and control the cell’s function. In normal cells, genes determine how cells should divide and grow at a controlled rate. A change in the gene – also known as mutation – of a single normal cell is the onset of cancer. Once cancer due to gene mutations has occurred, cells may begin to grow and multiply out of control.
In other words, cancer is the uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in any part of the body. Cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body. The area where cancer first starts in the body is called the primary cancer, or primary site. If cancer cells spread to another part of the body, it’s known as a secondary cancer, or metastasis. For example, cancer cells in the lung that travel to the bones and grow there is called metastatic lung cancer. It is not bone cancer unless the cancer started in the bones.